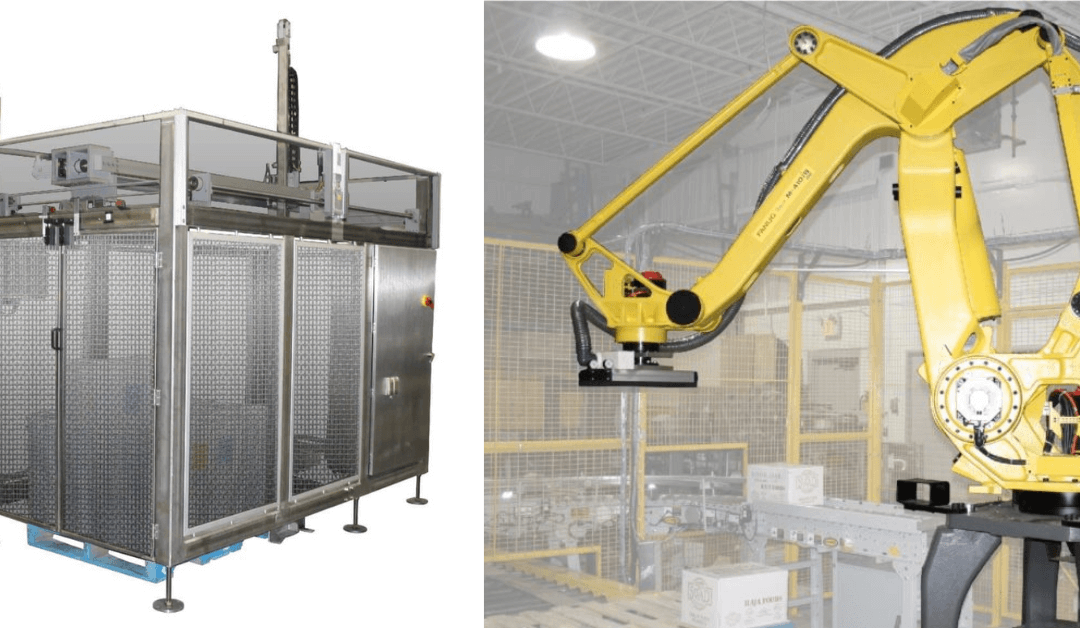
When it comes to optimizing your packaging line, choosing the right palletizing system is crucial. Whether you’re considering upgrading your current system or installing a new one, understanding the differences between robotic and conventional palletizers is essential. In this guide, we’ll explore the key features, benefits, and considerations for both types of palletizers to help you make an informed decision.
What Is a Palletizer?
A palletizer is a machine designed to automate the process of stacking products onto pallets. This process is essential in industries like food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods, where efficient and consistent palletizing can significantly impact productivity and cost.
What are Robotic Palletizers?
Robotic palletizers use robotic arms equipped with specialized grippers to pick and place products onto pallets. These systems are highly adaptable and can handle a wide variety of product types, sizes, and configurations. The robotic arm can be programmed to perform different palletizing tasks, making it a versatile solution for modern manufacturing and warehousing operations. There are the following advantages of robotic palletizers:
Flexibility and Versatility
Robotic palletizers are known for their flexibility. Unlike conventional palletizers, which are typically designed for specific tasks, robotic palletizers can be easily programmed to handle various products and palletizing patterns. This makes them an excellent choice for companies with diverse product lines or frequently changing packaging needs.
- Adapts to Different Products: Robotic palletizers can handle different sizes, shapes, and weights of products with minimal adjustments.
- Handles Multiple Palletizing Patterns: The ability to switch between different palletizing patterns quickly makes robotic palletizers ideal for companies that require custom stacking arrangements.
Precision and Accuracy
One of the standout features of robotic palletizers is their precision. The robotic arm, often equipped with advanced sensors, ensures that each product is placed accurately on the pallet. This level of precision reduces the risk of product damage and enhances overall pallet stability.
- Reduced Product Damage: With precise placement, products are less likely to be damaged during palletizing.
- Enhanced Pallet Stability: Accurate stacking results in more stable pallets, reducing the risk of toppling during transport.
Space Efficiency
Robotic palletizers are typically more compact than their conventional counterparts. This makes them an attractive option for facilities with limited space. Additionally, their modular design allows for easy integration into existing production lines without significant modifications.
- Compact Footprint: Ideal for facilities with space constraints.
- Easy Integration: Can be seamlessly integrated into existing production lines.
Maintenance and Operational Costs
While robotic palletizers offer numerous advantages, it’s important to consider the maintenance and operational costs. Robotic systems tend to have higher upfront costs, but their long-term benefits, such as reduced labor costs and lower product damage, often outweigh these initial expenses.
- Higher Initial Investment: Robotic palletizers typically require a higher upfront investment compared to conventional systems.
- Lower Long-Term Costs: Reduced labor and product damage can lead to significant cost savings over time.
What are Conventional Palletizers?
Conventional palletizers are mechanical systems that automatically stack products onto pallets using layers and patterns. These machines have been a staple in manufacturing and warehousing environments for decades. They operate through a series of conveyor belts, layer-forming mechanisms, and lifting devices to arrange products in precise stacks. There are the following advantages of conventional palletizers.
Speed and Throughput
Conventional palletizers are known for their speed. These systems are designed to handle high volumes of products at a rapid pace, making them ideal for industries with high throughput requirements. If your production line demands speed above all else, a conventional palletizer might be the better choice.
- High-Speed Operations: Capable of handling large volumes of products quickly.
- Ideal for High Throughput: Best suited for industries with high production demands.
Reliability and Durability
Conventional palletizers are built to last. These systems are often constructed with heavy-duty materials and designed for continuous operation. As a result, they are highly reliable and require less frequent maintenance compared to robotic systems.
- Robust Construction: Built for durability and long-term use.
- Low Maintenance Requirements: Requires less frequent maintenance, resulting in lower downtime.
Cost Considerations
One of the main advantages of conventional palletizers is their lower upfront cost. For companies with budget constraints, a conventional palletizer can be an attractive option. However, it’s important to weigh this against the potential for higher long-term costs, such as increased labor and product damage.
- Lower Initial Cost: Generally more affordable upfront compared to robotic systems.
- Potential for Higher Long-Term Costs: Increased labor and product damage may lead to higher expenses over time.
Limited Flexibility
While conventional palletizers excel in speed and durability, they lack the flexibility of robotic systems. These machines are typically designed for specific tasks and may require significant modifications to accommodate different products or palletizing patterns.
- Task-Specific Design: Best suited for specific, unchanging tasks.
- Challenging to Reconfigure: Modifying the system for new products or patterns can be time-consuming and costly.
Conventional vs Robotic Palletizing
| Feature | Robotic Palletizers | Conventional Palletizers |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, can handle different product sizes, shapes, and patterns. | Less flexible, usually designed for specific product types and patterns. |
| Speed | Generally slower than conventional palletizers, but speed can be increased with multiple robots. | Typically faster for high-volume, uniform product lines. |
| Footprint | Compact footprint; can fit into smaller spaces due to their flexible design. | Requires more space due to conveyor systems and fixed setups. |
| Complexity of Operation | Can handle complex palletizing tasks with ease, including mixed pallet loads. | Less adept at handling complex or varied palletizing tasks. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment due to advanced technology, but cost-effective in the long run. | Lower initial cost, but may require more maintenance and operational costs over time. |
| Maintenance | Easier to maintain with fewer moving parts, though specialized knowledge may be required. | More moving parts mean more frequent maintenance, though generally easier to service. |
| Scalability | Easily scalable by adding more robots as needed. | Scalability is limited and typically requires significant changes to equipment. |
| Energy Efficiency | Generally more energy-efficient due to advanced motors and controls. | Can be less energy-efficient due to older technologies and more moving parts. |
| Safety | Advanced safety features, including sensors and barriers, to protect workers. | Generally safe, but relies more on physical barriers and mechanical systems for safety. |
| Ease of Programming | Requires specialized programming knowledge, but modern systems often include user-friendly interfaces. | Simpler to set up with standard controls, but less adaptable to changes. |
| Adaptability to Product Changes | Easily adaptable to product changes, with minimal downtime required. | Adaptability is limited; significant reconfiguration may be required. |
| Labor Requirements | Reduces labor needs significantly, as robots can operate autonomously. | May require more manual intervention, especially for changeovers. |
| Return on Investment (ROI) | Higher ROI over time due to efficiency and flexibility. | Lower initial cost but potentially higher long-term costs due to maintenance and inefficiency. |
| Typical Industries | Widely used in industries with varied product lines like food & beverage, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods. | Common in industries with consistent product lines, such as automotive, chemicals, and building materials. |
This table provides a side-by-side comparison to help understand the key differences between robotic and conventional palletizers.
Key Considerations for Choosing Between Robotic and Conventional Palletizers
Production Volume and Speed
If your production line operates at high speeds and requires the handling of large volumes, a conventional palletizer may be the better option. These machines are designed to keep up with fast-paced environments, ensuring that your production line remains efficient and productive.
- High Volume, High Speed: Conventional palletizers are ideal for large-scale operations.
- Lower Volume, High Flexibility: Robotic palletizers excel in environments where flexibility is key.
Product Diversity
For companies that handle a wide range of products, robotic palletizers offer unmatched versatility. Their ability to adapt to different product sizes, shapes, and palletizing patterns makes them a valuable asset in industries with diverse product lines.
- Wide Range of Products: Robotic palletizers are ideal for companies with diverse product lines.
- Limited Product Range: Conventional palletizers are best suited for companies with a narrow range of products.
Space Constraints
If space is a concern in your facility, robotic palletizers may be the more practical choice. Their compact design and ability to integrate seamlessly into existing production lines make them a space-efficient solution.
- Limited Space: Robotic palletizers are a better fit for facilities with space constraints.
- Ample Space: Conventional palletizers require more space but offer high-speed operations.
Budget Considerations
Budget is often a determining factor when choosing between robotic and conventional palletizers. While robotic systems may require a higher initial investment, their long-term cost savings can make them a more economical choice in the long run. Conversely, conventional palletizers offer a lower upfront cost, which can be appealing for companies with limited budgets.
- High Initial Investment: Robotic palletizers require a higher upfront investment but offer long-term savings.
- Lower Initial Cost: Conventional palletizers are more affordable initially but may incur higher long-term costs.
Which Palletizer Is Right for You?
Choosing between robotic and conventional palletizers ultimately depends on your specific needs and priorities. If flexibility, precision, and space efficiency are at the top of your list, a robotic palletizer may be the best fit. On the other hand, if speed, durability, and lower upfront costs are more important, a conventional palletizer could be the way to go.
When making your decision, consider factors such as production volume, product diversity, available space, and budget. By carefully evaluating these aspects, you can select the palletizer that will optimize your packaging line, improve efficiency, and reduce costs.
Investing in the right palletizing system is a critical decision that can have a significant impact on your business’s productivity and profitability. Whether you choose a robotic or conventional palletizer, the key is to select a solution that aligns with your operational goals and long-term vision.
Why AFA Systems?
At AFA Systems, we understand the diverse packaging needs of our clients, which is why we offer a comprehensive range of cutting-edge packaging machinery solutions:
- Cartoning Machines: Designed for efficient and precise packaging, suitable for various products.
- Vertical and Horizontal Cartoners: Ideal for space-saving and versatile packaging configurations.
- Case Packer Machines: Highly adaptable for different packaging sizes and formats.
- Robotic Top Load Case Packers: Combining automation with flexibility for complex packing requirements.
- Tray and Carton Formers: Essential for shaping trays and cartons to exact specifications.
- Palletizer Machines: Efficiently stacking products for secure transportation.
- Case Erectors and Sealers: Ensuring robust packaging with consistent performance.
- Packaging Robots: Enhancing precision and speed in packaging lines.
- Used Packaging Equipment: Cost-effective solutions with AFA’s trusted reliability.
Each of these solutions is engineered to improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and ensure that your packaging operations are seamless and effective. Whether you’re upgrading existing lines or starting fresh, AFA Systems provides the expertise and innovation to meet your unique needs. Visit AFA Systems to explore more about how we can support your packaging goals.